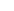What Does a Health Data Analyst Do?
What does a Health Data Analyst do?
A Health Data Analyst plays an increasingly important role in modern healthcare. With the rise of digital patient data, electronic health records (EHRs), wearables, and other data sources, there is a growing need for specialists who can transform this vast amount of information into valuable insights.
Collecting and structuring health data
The first task of a Health Data Analyst is to collect data from various sources. Think of medical records, administrative systems, patient monitoring, lab results, and even data from apps or wearable technology. This data is then cleaned, validated, and structured to make it suitable for further analysis.
Analyzing and interpreting healthcare data
Using statistical models, dashboards, and analytical tools, the Health Data Analyst examines trends and patterns in the data. This may include tracking disease outbreaks, monitoring treatment outcomes, or predicting healthcare needs. Software such as SQL, Python, R, or specialized BI tools is often used for this purpose.
Insights for better patient care
The ultimate goal of a Health Data Analyst is to provide insights that support better decision-making. This could involve reducing wait times, improving treatment pathways, or identifying risk factors for chronic diseases. Through data analysis, hospitals, healthcare institutions, and governments can implement more targeted policies and operate more efficiently.
Contributing to cost control and process optimization
In addition to improving patient care, the Health Data Analyst also plays a key role in controlling healthcare costs. By optimizing processes and identifying waste, healthcare organizations can operate more efficiently. Think of analyzing medication use, hospital admissions, or logistical processes within the healthcare chain.
Multidisciplinary collaboration
Health Data Analysts often work together with doctors, nurses, policymakers, IT specialists, and data scientists. They act as a bridge between medical knowledge and data analysis. A solid understanding of both medical terminology and data analysis techniques is therefore essential.
Growing demand for Health Data Analysts
Due to the digitalization of healthcare and the rise of personalized medicine, the demand for Health Data Analysts is growing rapidly. Organizations in primary care, hospitals, mental health services, health insurers, and government agencies are looking for professionals who can translate data into action-oriented insights.
Conclusion
A Health Data Analyst has become indispensable in modern healthcare. By using data smartly, this specialist contributes to better care quality, more efficient processes, and healthier populations. It is a field at the intersection of technology, data, and healthcare, with a significant societal impact.

A Day in the Life of a Health Data Analyst
Health Data Analysts play a key role in modern healthcare. They are the bridge between data and better patient care, between numbers and human impact. But what exactly do they do in a day? Let’s walk through a typical workday of Lisa, a Health Data Analyst at a large university medical center.
08:00 – Starting the day with coffee and dashboards
Lisa’s workday starts calmly. She opens her laptop with a cup of coffee by her side and logs into the dashboard she built the day before. She checks whether the automated data streams from the night have come in correctly. Today, she’s mainly looking at trends in readmissions within 30 days after discharge.
“Sometimes you spot something unusual early in the morning: a spike in readmissions or an anomaly in medication use. That immediately sets the direction for your day.”
09:00 – Daily stand-up with the data and IT team
Lisa joins the daily stand-up meeting. Together with data engineers, other analysts, and a project manager, she discusses the progress of ongoing projects. They’re working on a new algorithm to better predict the risk of hospital admissions for chronic patients.
“We align on responsibilities, identify bottlenecks, and exchange ideas. Collaboration between data experts and IT is crucial to successfully delivering projects.”
10:00 – Analyzing clinical performance data
After the stand-up, Lisa dives into a specific dataset concerning postoperative complications. She works with a surgical resident to investigate whether certain complications occur more frequently with specific procedures or patient groups.
She uses statistical software like R or Python to find significant correlations. She also looks at factors such as age, BMI, and comorbidities. The results are later discussed with the medical team.
“It’s very rewarding when you can provide doctors with insights they can truly use.”
12:30 – Lunchtime walk with a colleague
After an intensive morning, it’s time to get some fresh air. Together with a colleague from quality management, Lisa takes a walk around the hospital. They talk about an internal conference on data-driven care and discuss new tools like predictive modeling in primary care.
“Stepping away from the screen, but still exchanging thoughts about our field. That keeps me sharp and inspired.”
13:30 – Meeting with the management team
In the afternoon, Lisa joins a meeting with the cardiology department’s management team. She presents a report on waiting times, process durations, and occupancy rates. Her analyses show there’s room for improvement in the pre-operative screening, where delays are currently occurring.
“Data only becomes valuable when it leads to better decision-making. This is where you see analytics truly making an impact.”
15:00 – Working on a data visualization for the annual report
Time for some creativity. Lisa is working on an interactive data visualization for the hospital’s annual report. The goal: to provide insights into the number of treatments, patient satisfaction, and quality indicators in an accessible way.
She uses tools like Power BI or Tableau to present the figures not only accurately but also attractively.
“Good visualizations make data understandable for everyone – from executives to policymakers.”
16:30 – Catching up on emails and planning ahead
At the end of the day, Lisa checks her inbox. She answers questions from colleagues, schedules a meeting for a new research project, and prepares a to-do list for tomorrow. She also makes a short note in her logbook: what went well, what could be improved?
“Structure and reflection are important in a field where you work with so many details.”
17:30 – Ending the day with a sense of accomplishment
The laptop closes. Lisa walks out of the hospital with satisfaction. She has contributed to better care, with her expertise in data as her guiding compass.
“What I love most? That my work – no matter how technical – ultimately contributes to people’s health.”
The impact of a Health Data Analyst
The work of a Health Data Analyst is diverse, content-rich, and meaningful. Whether it’s about improving processes, supporting physicians, or contributing to strategic decisions: they ensure that data becomes more than just numbers – it becomes a driving force behind better care.

What tools does a Health Data Analyst use?
Data Analysis Tools
A modern Health Data Analyst uses a wide range of powerful data analysis tools to process, interpret, and translate health data into actionable insights. Languages such as Python and R are essential for manipulating datasets, performing statistical calculations, and building predictive models.
Additionally, statistical software packages like SPSS, SAS, and SAS Viya remain relevant for health analyses, especially when testing hypotheses and conducting regression analyses. These tools are particularly useful in clinical research and epidemiological studies.
Increasingly, machine learning technologies are also being used to uncover patterns in medical datasets. Think of predictive models that help estimate the risk of chronic diseases or algorithms that detect abnormal patterns in lab results. Thanks to the integration of these smart analytical methods, decisions can be made faster and more accurately.
Health Information Systems
Health information systems are the backbone of data collection in healthcare. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) such as Epic, Cerner, and Greenfield Health provide standardized access to patient data. These systems are used to document medical information, track treatment pathways, and evaluate patient outcomes.
The modern Health Data Analyst increasingly works with integrated systems that include AI components. This enables the generation of real-time insights and early detection of anomalies. The linking of clinical data with external data sources such as population statistics and socio-demographic information also provides deeper insight into health issues at the population level.
Terms like "interoperability" and "data integration" have also become increasingly important. A good analyst knows how to combine data from different sources into one reliable and usable whole, with attention to privacy and ethics.
Visualization Tools
Translating complex medical data into understandable information is a crucial part of a Health Data Analyst’s role. Visualization tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik Sense assist in this by generating interactive dashboards, charts, and maps.
These tools make it possible to visually present trends in hospital admissions, highlight risk areas on a map, or compare treatment outcomes over time. By making data visually accessible, policymakers and healthcare providers can make quicker and better-informed decisions.
Advanced techniques such as automated data updates, real-time dashboards, and automated reporting ensure that the information is always up to date. Moreover, new developments in automated data visualization offer the ability to detect patterns that previously remained hidden.

What is the salary of a Health Data Analyst?
The salary of a Health Data Analyst can vary based on factors such as experience, location, type of healthcare institution, and the complexity of the data being handled. Health Data Analysts play a crucial role in analyzing medical and healthcare-related data to improve the quality of care, reduce costs, and make processes more efficient. Below is an overview of the expected salary levels by experience level.
Entry Level (Junior Health Data Analyst)
A Junior Health Data Analyst, often a recent graduate in a field such as health sciences, biomedical sciences, data science, or a related discipline, typically earns between €2,800 and €3,800 per month. At this level, tasks often include collecting, cleaning, and visualizing health data, such as from electronic health records (EHRs), claims systems, or medical registries. Junior analysts often work with tools like Excel, SQL, and basic BI tools such as Power BI or Tableau.
Mid-level (Health Data Analyst)
A Health Data Analyst with 2 to 5 years of experience usually earns between €3,800 and €5,000 per month. They are familiar with analyzing complex datasets from various healthcare information systems, developing dashboards, and creating policy reports. They often use more advanced tools like Python, R, SAS, or SPSS, along with knowledge of healthcare information systems and standards (such as HL7 or SNOMED). Analysts at this level provide valuable insights for quality improvement, capacity planning, and policy development.
Senior Level (Senior Health Data Analyst)
A Senior Health Data Analyst with more than 5 years of experience earns on average between €5,000 and €6,500 per month. They take a leading role in research projects, policy analyses, or the development of predictive models for, for example, patient flow or readmissions. They often work at the intersection of data analysis and policy and advise management or medical staff based on their insights. Senior analysts have in-depth knowledge of both data analysis and the Dutch healthcare system.
Lead Health Data Analyst
In larger healthcare institutions, public health services (GGD), or national knowledge organizations, Lead Health Data Analysts fulfill a coordinating or strategic role. They typically earn between €6,500 and €8,000 per month. These professionals lead a team of analysts, manage large data projects, and work closely with policymakers, IT specialists, and medical staff. They are often involved in strategic themes such as healthcare digitalization, population health management, or data-driven prevention.
Location and Sector
Location and organizational structure influence salary levels. Health Data Analysts working at academic hospitals, national health insurers, public health services (GGDs), or research institutions often earn more than analysts at smaller care providers. In urban areas such as Amsterdam, Utrecht, and Leiden, salaries are generally higher, partly due to the presence of large healthcare institutions and data-intensive projects.
Education and Skills
An academic background in health data, biostatistics, or epidemiology provides a strong foundation. Experience with data analysis platforms (such as R or Python), medical terminology, privacy legislation (such as GDPR), and knowledge of EHR systems and healthcare standards (such as DBCs and ICD codes) is in high demand. Skills in data storytelling, visualization, and translating data into policy advice also increase the market value of a Health Data Analyst.
Career path and growth opportunities
Career Path and Growth Opportunities as a Health Data Analyst
A career as a Health Data Analyst not only offers a solid start in the world of data and healthcare, but also plenty of opportunities for growth and specialization. As you gain more experience, you can develop into a valuable asset within the field – with ample opportunities to progress into senior roles or leadership positions.
From Junior to Senior: Advancing with Experience
Many professionals start at junior level, where they further refine their skills in data collection, analysis, and reporting. With a few years of practical experience, supplemented by advanced training or certifications, the opportunity arises to move into mid-level and senior roles. In these positions, you take on more responsibilities, tackle complex challenges, and often serve as a sparring partner for policymakers or healthcare professionals.
Leadership Roles and Project Management
For those interested in coordination or team leadership, there are opportunities to grow into roles such as data analysis team lead, project manager, or even department head. These positions require not only analytical expertise but also skills in communication, strategy, and leadership.
Specialization Opens Doors to Niche Roles
Specialization is a powerful way to stand out and add value within health data. Consider deepening your expertise in areas such as genomics, epidemiology, health psychology, or clinical informatics. By building in-depth knowledge in a niche field, you can take on unique roles – from Bioinformatician to Epidemiological Analyst or specialist in AI applications in healthcare.
Lifelong Learning as the Key to Growth
The world of health data is constantly evolving. New technologies, scientific insights, and laws and regulations drive ongoing change. Those who continue to develop through training, conferences, certifications, or master's programs increase their chances of advancement and remain attractive in the job market.
A Future Full of Possibilities
Whether you choose a path toward management, specialized expertise, or innovative applications of data in healthcare: the career path of a Health Data Analyst is versatile and future-proof. With the right mindset and investment in your development, you can become an indispensable part of the healthcare system of tomorrow.

Education and Certification
Education
For a successful career as a Health Data Analyst, a strong academic foundation is essential. Most professionals in this field hold at least a bachelor's degree in areas such as health informatics, statistics, biomedical sciences, epidemiology, or information science. These studies provide an in-depth understanding of medical data, analytical techniques, and data-driven decision-making in the healthcare sector.
In a health informatics program, for example, students learn how to effectively use electronic health records (EHRs) to improve the quality of care. Statistics and data-related programs focus more on mathematical models, predictive analytics, and data visualization. Increasingly, students are also choosing interdisciplinary programs that combine healthcare with data science, which aligns well with the growing demand for professionals with combined expertise in healthcare and technology.
Master's programs are also gaining popularity. A Master in Health Informatics or a Master in Data Science with a specialization in healthcare data can provide a significant advantage in the job market. These advanced programs focus on sophisticated analytical techniques, artificial intelligence in healthcare, and the ethical and legal aspects of data usage.
Certifications
In addition to a completed degree, certification plays an increasingly important role in helping Health Data Analysts stand out. Employers value demonstrable, up-to-date knowledge of tools, technologies, and systems commonly used in the healthcare sector.
Various relevant certifications are available. For example, organizations like the Data Science Council of America (DASCA) offer certifications focused on data analysis skills, such as the Certified Data Scientist™ program. Such certifications highlight an analyst’s technical competence and improve the chances of obtaining a more senior position.
Additionally, providers of electronic health information systems, such as Epic and Cerner, offer their own certification programs. These certificates demonstrate in-depth knowledge of specific systems and are often a requirement for roles in larger healthcare institutions. Certification in, for instance, Epic Clarity Data Model or Cerner PowerInsight can lead to specialized roles such as Clinical Data Analyst or EHR Data Specialist.
More general data analysis tools such as SQL, Python, R, Tableau, and Power BI also offer certification opportunities that align well with the day-to-day responsibilities of a Health Data Analyst. By investing in targeted certifications, professionals not only stay up-to-date but also increase their employability and career advancement opportunities.

Networking and Industry Organizations
Why join industry organizations as a data professional?
For professionals in health data and data analysis, staying connected to the field is essential. A powerful way to do this is by joining industry organizations and professional networks. These memberships open the door to valuable networking opportunities, up-to-date knowledge sharing, and ongoing professional development.
Stay informed about trends and developments
By actively participating in professional organizations, you stay well-informed about the latest trends in health data, AI applications in healthcare, data quality, privacy regulations (such as GDPR), and system interoperability. Seminars, webinars, workshops, and conferences are regularly organized where experts share their knowledge.
Expand your network in the world of data and healthcare
Whether you work as a Health Data Analyst, Data Steward, Data Scientist, or Data Manager Public Space — networking with like-minded peers in your field offers great value. You build lasting connections with other professionals, researchers, policymakers, and vendors. These relationships can lead to new career opportunities, collaborative projects, or even participation in innovative research initiatives.
Access to exclusive resources and educational content
Many industry associations offer their members access to specialized resources such as whitepapers, research reports, tools, and training. This is ideal for those who want to continue developing themselves and stay relevant in a rapidly changing field. Young professionals also benefit, for example through mentoring programs or peer learning groups.
Professional visibility and credibility
An active membership enhances your professional profile. It shows that you take your profession seriously and are committed to ongoing improvement. This can have a positive effect on your credibility with clients, employers, or partners. It shows that you're part of something bigger: a community that values quality, innovation, and knowledge sharing.
Join and strengthen your position in the job market
The job market for data professionals in the healthcare sector is constantly evolving. By being a member of an industry organization, you increase your chances of landing interesting assignments or taking the next step in your career. Additionally, you'll more easily connect with organizations looking to lead in data-driven work.

Impact and Social Relevance
The Social Relevance of a Health Data Analyst
In a time when pressure on healthcare is increasing, the Health Data Analyst plays a key role in improving care quality, increasing efficiency, and keeping healthcare costs manageable. By analyzing medical and organizational data, these professionals provide valuable insights that lead to better-informed decisions at all levels within the healthcare sector.
Concrete Impact on Patient Care
The insights generated by a Health Data Analyst have a direct impact on the quality of patient care. Think of identifying trends in treatment outcomes, detecting bottlenecks in care processes, and optimizing patient journeys. Thanks to data-driven care, interventions can be made more quickly and effectively, resulting in better health outcomes and higher patient satisfaction.
Efficiency and Cost Control
By identifying inefficiencies in processes and logistics, a Health Data Analyst helps healthcare institutions work smarter. Think of reducing unnecessary readmissions, optimizing staff deployment, or organizing care pathways more efficiently. In doing so, the analyst contributes to substantial cost savings without compromising care quality.
Prevention and Public Health
The social value of a Health Data Analyst goes beyond individual healthcare institutions. At the level of public health and prevention, data analyses provide insights that help policymakers intervene more effectively. For example, in the early detection of epidemics, identifying risk groups, or evaluating prevention programs.
Supporting Policy and Strategy
The strategic value of health data is increasingly recognized. Health Data Analysts support executives, policymakers, and regulators with reports and dashboards that inform decision-making. As a result, they contribute to more transparency, accountability, and future-proof choices in a dynamic healthcare landscape.
Growing Demand and Social Relevance
Due to the digitalization of healthcare, the amount of available data is growing exponentially. At the same time, there is a rising demand for professionals who can interpret this data and translate it into actionable insights. The role of Health Data Analyst is therefore not only crucial but also extremely socially relevant and future-proof.

How to Become a Health Data Analyst?
How to Become a Successful Health Data Analyst?
The role of Health Data Analyst is rapidly emerging, driven by the increasing digitalization of healthcare. Hospitals, care institutions, insurers, and government agencies are increasingly relying on data to make better decisions. But how do you build a career as a Health Data Analyst? Here you’ll find a step-by-step guide to successfully follow this path.
1. Start with a relevant academic background
The first step is obtaining a suitable education. Think of a university or applied sciences degree in fields like Health Sciences, Biomedical Sciences, Medicine, Data Science, or Computer Science. Programs such as Medical Informatics or Healthcare Technology are also excellent starting points. A strong foundation in statistics, data analysis, and programming languages like R or Python is essential.
2. Gain practical experience through internships or junior roles
In addition to theoretical knowledge, practical experience is crucial. An internship at a hospital, health insurer, or research institute gives you the opportunity to experience healthcare data analysis up close. Junior roles such as Junior Health Data Analyst, Data Steward, or Medical Researcher offer a good entry into the field and help you gain insights into processes, data quality, and policy-related issues.
3. Specialize and keep developing yourself
The world of healthcare data is evolving rapidly. By deepening your knowledge in areas such as EHRs (Electronic Health Records), privacy regulations (such as GDPR), predictive analytics, and machine learning, you remain relevant. Taking postgraduate courses, training programs, or certifications – for example in Health Informatics or medical data analysis – will strengthen your profile.
4. Build your network within the healthcare and data world
Networking is essential for building a career as a Health Data Analyst. Attend conferences, participate in webinars, and join (online) communities focused on healthcare analytics and data science. By exchanging experiences and getting inspired by others, you’ll discover new opportunities and stay up to date with the latest developments in the field.
5. Aim for impact and stay curious
As a Health Data Analyst, you work on projects that truly matter. You help improve healthcare, make processes more efficient, and enhance patient safety. A curious, analytical mindset and the motivation to do meaningful work are key success factors in this profession. Keep asking questions, think in solutions, and don’t be afraid to critically evaluate data and processes.
A future-proof choice
The demand for Health Data Analysts is growing rapidly. With the right education, practical experience, and continuous development, you can build a career with strong prospects and social relevance. Whether you work in a hospital, for the government, or in the private sector – your work makes a difference in the healthcare of tomorrow.

Case Study: The Role of Health Data Analyst
Background
The City Hospital aims for continuous improvement of patient care through data-driven decision-making. Although there was an abundance of health data available, this information was rarely used to actually improve care. The available data often remained unused in dashboards or databases, while it could have added significant value to strategic decisions.
The Challenge
Health data is both complex and sensitive. The hospital faced several obstacles: integrating different data sources, safeguarding privacy, and finding ways to extract relevant insights from the data without violating laws and regulations. The challenge was therefore to extract usable information from the data that could demonstrably contribute to better care—within ethical and legal boundaries.
The Approach of the Health Data Analyst
Liam, Health Data Analyst at the City Hospital, approached this challenge in a structured way. He designed an analysis process that considered privacy laws and ethical standards from the very beginning. By using advanced analytical techniques and machine learning, he was able to discover relevant patterns and trends in patient data.
But Liam did more than just analyze. He worked closely with doctors and nurses to make the outcomes of his analyses understandable and directly applicable in practice. This enabled healthcare providers to confidently act on the insights.
The Result
Thanks to the insights from Liam's analyses, the hospital was able to implement targeted improvements in care delivery. Think of more efficient treatment paths, more focused use of staff, and quicker identification of patient risks. This led not only to demonstrably better outcomes for patients but also to a more effective use of resources.
In addition, a cultural shift occurred within the hospital: data was increasingly seen as a valuable tool in decision-making. Trust in data-driven work grew, laying the foundation for further innovation in healthcare.

Looking for a Health Data Analyst?
For a small fee, you can easily post your job openings on our platform and reach our large, relevant network of data and analytics professionals. Applicants respond directly to you, without any intermediaries.
On DataJobs.nl, we connect supply and demand in the data and analytics job market directly—without middlemen. You won’t find job listings from recruitment agencies on our site. Visitors can view all vacancies for free and without an account, and apply directly.
See the options for posting vacancies here. Questions? Get in contact with us!

Op zoek naar een uitdaging in data & analytics?
Bekijk hier alle actuele kansen! See vacancies- What Does a Health Data Analyst Do?
- A Day in the Life of a Health Data Analyst
- What tools does a Health Data Analyst use?
- What is the salary of a Health Data Analyst?
- Career path and growth opportunities
- Education and Certification
- Networking and Industry Organizations
- Impact and Social Relevance
- How to Become a Health Data Analyst?
- Case Study: The Role of Health Data Analyst
- Vacancies for Health Data Analysts
- Looking for a Health Data Analyst?